Artificial Intelligence Based Statistical Process Control for Monitoring and Quality Control of Water Resources: A Complete Digital Solution
Keywords:
Artificial intelligence, Machine Learning, data analysis, statistical process control, SPC charts, DAM projectsAbstract
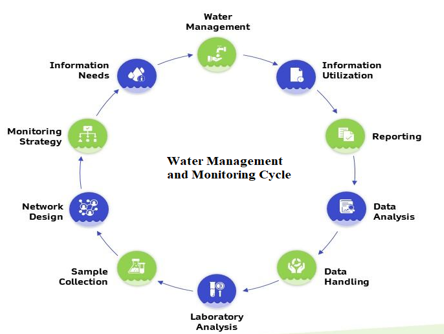
In order to monitor water resource projects, this study examines the use of Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts in the context of dam projects. A survey of the body of knowledge on the subject of water resource project monitoring methods is the first stage in the research project. In this research, we'll focus on the advantages of use SPC charts to achieve that objective. Water resource projects are crucial pieces of infrastructure, and as such, they need constant supervision to ensure that they continue to operate properly and efficiently. SPC, or statistical process control, is a technique used for quality control and process monitoring across a wide range of industries. On the other hand, traditional SPC methodologies might not be suitable for real-time monitoring of water resource projects due to the complexity and unpredictability of water systems. Artificial intelligence (AI)-based methods have lately gained attention as a potential solution to these issues. In this paper, we provide an artificial intelligence-based SPC framework for real-time monitoring and quality control of projects involving water resources using a case study of a dam building project. The framework that has been proposed combines SPC with machine learning techniques to automatically detect anomalies and predict how the system will behave in the future. The results show that the artificial intelligence-based SPC framework outperforms the traditional SPC techniques in terms of timeliness, accuracy, and efficiency. The framework has the potential to improve the management and long-term profitability of water resource projects, which would ultimately aid in preserving the environment and the general public's health.
Downloads
References
Al-Mutairi, N. F. (2016). Statistical Process Control Techniques for Effective Water Quality Management: A Review. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 8(06), 654-668.
Bhatia, S., Sharma, R. K., & Kumar, S. (2019). Statistical process control charting and performance analysis for water treatment plant. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 27, 14-22.
El-Bahrawy, A., & Ismail, N. (2018). Application of statistical process control charts in the management of water distribution networks. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology-Aqua, 67(1), 19-30.
Gong, M., & Li, X. (2020). Research on the application of SPC control charts in water quality monitoring. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1534(1), 012064.
Lee, K. C., Lin, Y. F., & Chen, Y. C. (2017). Applying statistical process control to monitor water quality in a river network. Journal of Hydrology, 547, 322-331.
Li, J., Li, C., Li, Z., & Sun, X. (2018). A review of statistical process control for water treatment processes: principles, methods and applications. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 11, 148-158.
Padmanabhan, G., & Pandian, P. K. (2019). Application of statistical process control in water quality monitoring. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(3), 1623-1632.
Sankar, K., & Elanchezhian, R. (2018). Statistical process control application in monitoring water quality parameters of a river. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology-Aqua, 67(7), 708-716.
Vinoth, K. J., & Sowmiya, S. (2021). Statistical process control analysis for monitoring water quality parameters in wastewater treatment plant. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 1-9.
Zhou, Y., Tang, C., Wu, Z., Wu, X., & Wang, J. (2019). Application of statistical process control in water quality monitoring in drinking water supply system. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 27, 238-246.
Li, Y., Zheng, Y., Zhang, J., Li, X., & Wang, Y. (2021). An Integrated Quality Control Framework for Drinking Water Safety Management Based on Statistical Process Control and Multivariate Time Series Modeling. Water, 13(5), 676.
Ouyang, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, X., & Sun, G. (2020). Statistical Process Control in Water Quality Management: A Bibliometric Analysis. Water, 12(8), 2178.
Zhang, J., Liu, X., Zhou, J., & Song, J. (2019). An application of statistical process control charts for water quality management in river systems. Water Science and Engineering, 12(1), 16-23.
Wu, X., Sun, C., Zhang, J., Wang, J., & Liu, S. (2020). Using statistical process control charts for monitoring water quality in a wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(4), 4166-4174.
Chen, C., Zhang, J., & Zhang, X. (2019). Statistical process control for water quality monitoring in industrial parks. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 14, 100337.
Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., & Lu, Q. (2018). Real-time monitoring of water quality for drinking water safety using multivariate statistical process control. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 18(4), 1294-1304.
Su, C., & Chen, Y. (2020). Integration of statistical process control and machine learning for real-time monitoring of water quality in distribution systems. Water, 12(12), 3376.
Li, Z., Li, Y., & Li, X. (2020). An integrated quality control framework for drinking water safety management based on principal component analysis and statistical process control. Water Science and Technology, 81(1), 104-114.
Zhang, J., Liu, X., Zhou, J., & Yang, H. (2021). Applying statistical process control for monitoring and evaluating water quality in water distribution systems. Journal of Hydrology, 595, 125816.
Liu, X., Zhang, J., Zhou, J., & Chen, C. (2019). Water quality monitoring in distribution systems using statistical process control charts. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(15), 14902-14910.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





